Inflammasome Activation Pathways
Click on Signal 1 shown in the Explore Pathways box below to see the signaling pathways that lead to the transcription of IL-1 beta and IL-18. Then click on Signal 2 to see the factors that can provide a second signal for inflammasome activation and subsequent processing and secretion of IL-1 beta and IL-18.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.
Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request.
You will be notified once it becomes available.

Featured Literature
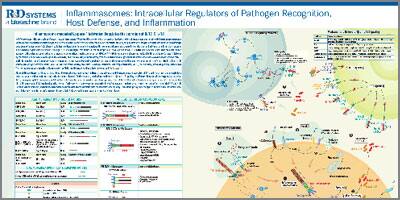
Inflammasomes: Intracellular Regulators of Pathogen Recognition, Host Defense, and Inflammation Poster
View PosterOverview of Inflammasome Activation
Nod-like receptors (NLRs) are a subset of cytoplasmic pattern recognition receptors that detect invading pathogens and initiate the innate immune response. NLRs are activated by bacterial, fungal, or viral molecules that contain pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) or by nonmicrobial danger signals (DAMPs) released by damaged cells. Upon activation, some NLRs oligomerize to form multiprotein inflammasome complexes that serve as platforms for the recruitment, cleavage, and activation of inflammatory caspases. Inflammasome oligomerization requires two signals, a priming signal that results in the transcription of IL-1 beta and IL-18, and a second signal that promotes indirect activation of the inflammasome such as reactive oxygen species (ROS), ion or membrane perturbations, or extracellular ATP. Four inflammasome complexes (NLRP1, NLRP3, IPAF, and AIM2) have been partially characterized. These complexes contain a specific NLR family protein or AIM2, the ASC and/or Cardinal adaptor proteins, and Pro-Caspase-1. In the NLRP3 inflammasome, the caspase recruitment domain (CARD) in Pro-Caspase-1 mediates its interaction with the ASC adaptor protein, which then interacts with NLRP3 through its pyrin (PYR) domain. Inflammasome oligomerization leads to the activation of Caspase-1, followed by the maturation and secretion of IL-1 beta and IL-18, and in some cases, an inflammatory form of cell death known as pyroptosis. Inflammasome/Caspase-1-dependent secretion of IL-1 beta and IL-18 induces the expression of secondary pro-inflammatory mediators and promotes immune cell recruitment to the infection site. Although IL-1 beta and IL-18 have a beneficial role in promoting inflammation and eliminating infectious pathogens, mutations that result in constitutive inflammasome activation and overproduction of IL-1 beta and IL-18 have been linked to autoinflammatory and autoimmune disorders.
To learn more, please visit our NOD-like Receptors and the Inflammasome Research Area.
Get Print Copy of this Pathway





